2020 Trends in Workforce Productivity and Collaboration
Organizations across all industries have experienced different levels of disruption as a result of the COVID-19 outbreak during the first half of 2020. The crisis has led to a surge in demand for real-time communications, with organizations looking to support an unprecedented number of employees working from home. It has also placed the spotlight on the frontline workforce, highlighting the critical role they play for the distribution and delivery of goods and services.
For many organizations, digital channels and frontline workers have proven critical for business continuity during the quarantine. The impact of the outbreak and the need to comply with physical distancing guidelines is also making the use of voice and contactless interfaces in the workplace even more relevant. These three trends highlight the relevance that the digitalization of the customer and employee experiences will have in the post-pandemic workplace. This should have a positive impact for the communications PaaS segment, with organizations leveraging the use of programmable communications to support their digital transformation initiatives.
451 Research’s Q4 View of the Market – What We Said
451 Research’s 2020 Trends in Communications, Connectivity and Collaboration Technologies
Our updated evaluation of the original trends follows below.
Source: 451 Research, 2019
COVID-19 Will Have a Significant Impact in the Workplace
451 Research believes that the transition into digital businesses for companies across all industries will accelerate as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic. We expect this trend will outlive the crisis, resulting in increased investment in the technologies that underpin and support digital transformation initiatives – including real-time communications and voice and contactless interfaces. Below, we look at three emerging trends that are gaining momentum as a result of the outbreak and the impact we believe these will have for the digitalization of the customer and employee experiences.
-
VOICE USER INTERFACES AND PHYSICAL DISTANCING WILL PLAY A KEY ROLE IN THE POST-COVID-19 WORKPLACE
While previously perceived largely as a novelty or ‘nice to have’ features, the need to provide a safe work environment that complies with physical distancing guidelines will make the use of contactless interfaces more compelling, driving workplace adoption of voice user interfaces, intelligent assistants and biometric authentication.
Voice user interfaces and intelligent assistants such as Amazon Alexa, Apple Siri and Google Assistant have become standard features on consumer devices including smartphones, tablets, laptops and smart speakers. While still lagging the consumer segment, this trend was already extending to the enterprise segment prior to the outbreak. Examples include voice-enabled devices designed specifically for the workplace – including desk phones, meeting room equipment and hearable devices – and the integration of intelligent assistants such as AWS Alexa for Business, Cisco Webex Assistant, Google Assistant and Microsoft Cortana with meeting room equipment and team collaboration workflows.
This is evident from product updates in the past year from industry players such as AWS, Cisco, Google Cloud, Microsoft and Poly. These include the integration of Alexa for Business with Lifesize, which enables the use of voice commands for tasks such as booking a meeting room, dialing directory contacts and starting a meeting; Google Cloud, which expanded Google Assistant capabilities in G Suite and Meet devices to allow the use of voice commands for tasks such as dialing into a meeting; and Microsoft, which unveiled new Cortana features for Outlook mobile. Other examples include Poly, which announced that its Voyager 4200 headsets will integrate with Amazon Alexa and Alexa for Business; and Cisco, which earlier this year announced new capabilities in Webex Assistant for Meetings that allow the use of voice commands to automate meeting tasks.
Adoption of voice UIs in the workplace could gain added momentum as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, with organizations looking to provide a safe environment in compliance with ongoing physical distancing requirements. Vendors could seek to replicate the voice-first/voice-only product design used in smart speakers, incorporating contactless interfaces – including voice interfaces and gesture recognition – to replace remote control devices and touchscreen interfaces for meeting room and office equipment. The use of intelligent assistants could extend outside the conference room environment, with voice-enabled devices that can be deployed in building lobbies and other common areas to provide directions, logistics information and announcements; voice and contactless interfaces could also be used to operate elevators and equipment in office buildings, factories and warehouses.
Biometric authentication could further expand the use cases for voice and contactless interfaces in the workplace. For example, NEC’s biometric solutions – which include contactless technologies such as facial recognition, iris recognition, voice recognition and ear acoustic authentication – have been deployed to address a wide range of use cases, including corporate building entry and exit management. NEC is now developing facial recognition technology that can identify people even if they are wearing a mask, allowing building access without the need to remove it or touch any surface.
-
PROGRAMMABLE COMMUNICATIONS ARE EMERGING AS A CRITICAL COMPONENT FOR BUSINESS CONTINUITY
Communications PaaS (CPaaS) was already expanding in recent years beyond its core user base of developers and digital native companies and increasingly gaining traction in the mainstream enterprise segment. This trend could accelerate as a result of the COVID-19 outbreak, which is creating a sense of urgency for the digitalization of the customer and employee experiences.
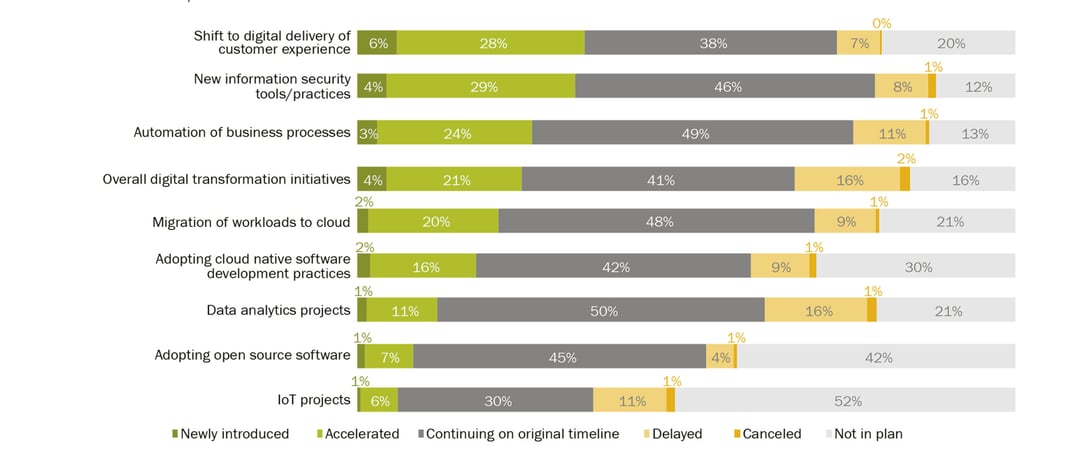
451 Research’s Voice of the Enterprise: Digital Pulse, Coronavirus Flash Survey June 2020 shows that, even though organizations are slowing down IT initiatives in several areas in response to the pandemic, a majority of respondents (62%) expect that digital transformation initiatives in their organizations will remain unaffected, or even accelerate. Four out of ten respondents (41%) expect these initiatives will continue according to their original timelines, while an additional two out of ten (21%) expect they will accelerate (see Figure 1).
Figure 1: Many Digital Transformation Initiatives Will Be Unaffected or Accelerate Due to COVID-19
Source: 451 Research’s Voice of the Enterprise: Digital Pulse, Coronavirus Flash Survey June 2020
Q: For each of the following types of technology initiatives, please indicate how they were affected at your organization, if at all. Base: All respondents
Like other segments, we expect that communications PaaS (CPaaS) will be adversely affected by the pandemic in the near term. The downturn can be explained by the effect of the COVID-19 pandemic in verticals such as hospitality and transportation; more specifically, the negative impact could come from ‘sharing’ economy companies such as Airbnb, Lyft and Uber, which have played a significant role in the growth performance of the CPaaS market to date. Conversely, other pockets of the aggregate CPaaS client portfolio have experienced a surge in demand as a result of the current environment – examples of this include grocery and food delivery services such as DoorDash and Instacart, and streaming services like Hulu and Netflix.
While this will drive increased demand, in the near term our CPaaS Market Monitor anticipates that the overall market growth will fall below our original projection. Long-term, the expectation is that the pandemic will have a net positive effect for the CPaaS segment as a result of the acceleration of digital transformation initiatives and the growing relevance of mobile technologies for use cases in both the consumer and enterprise segments.
-
THE PANDEMIC HAS PUT THE SPOTLIGHT ON FRONTLINE WORKERS
We have previously noted that, prior to the outbreak, organizations were paying more attention to frontline workers across different verticals including retail, manufacturing and healthcare. COVID-19 could accelerate this trend, with organizations looking to enable the digital experience and real-time communications for frontline workers to further automate and optimize business operations, reassessing the role they play in the customer journey.
The pandemic has put the spotlight on the frontline workforce (i.e., those workers who deal directly with customers or are closely involved in the production process), elevating many into essential roles. These include not just emergency responders and healthcare providers, but also grocery store and warehouse employees, truck drivers, and food and grocery delivery gig workers. The current crisis highlights the critical role they play for business continuity, particularly for the distribution and delivery of goods and services.
2020 Trends in Workforce Productivity & Collaboration
Digital transformation is causing businesses to rethink not only the technologies they use, but also their organizational design and patterns of collaboration they support. The demand for more flexible, extensible and purposeful forms of communication is growing, taking enabling technologies out of application silos with growing programmability, voice user interfaces, and AI and machine learning automation.
Key Findings:
-
According to 451 Research’s most recent Voice of the Enterprise: Digital Transformation survey, voice user interfaces and digital assistants are among the top disruptive technologies that organizations plan to adopt within the next 24 months.
-
Technology vendors are increasingly incorporating AI- and machine-learning- (ML-) enabled capabilities into their product roadmaps. Organizations with digital transformation initiatives expect these will have a significant impact in their operations over the next two years, according to the Digital Transformation survey.
-
Our CPaaS Market Monitor projects that the communications platform as a service (CPaaS) segment will grow at a 33% CAGR, reaching $11.4bn by 2023. The mainstreaming of programmable communications has already sparked M&A activity, with seven CPaaS-related deals so far in 2019, according to 451 Research’s M&A KnowledgeBase. We anticipate further consolidation in the CPaaS space in 2020 as real-time communications are integrated into more business applications.
Executive Summary
It’s clear we are entering a new era – one of personalization defined by consumers’ intensifying influence over not just what businesses produce, but also how it is produced and consumed. Neither revolutionary new ideas nor long periods of time are needed for markets to change; threats can emerge very rapidly from marginal improvements to the means of production and customer-engagement methods. The threat vectors for business success have multiplied and become more difficult to foresee. Businesses increasingly need to operate on the assumption that as change becomes a constant, having a highly and innately agile business operating model needs to be table stakes. That it’s not yet table stakes explains why so many businesses are being disrupted.
Businesses increasingly need to operate on the assumption that as change becomes a constant, having a highly and innately agile business operating model needs to be table stakes.
There needs to be a total rethink, on this basis, of what collaboration means across an enterprise. This agile operational model has to enable communication to be more integrated, automated and rapid within both tactical day-to-day and high-value structured workflows and processes. An important element of this is businesses realizing that their organizational silos, the technologies supporting them, and the management, organizational theory and practices that have grown up around them are strong impediments. Businesses need the technologies to fundamentally rethink how they organize and speak among themselves and externally with their customers and partners.
We see signs of more businesses realizing this imperative. As such, in 2020 we expect to witness the continuance of some of the trends we’ve seen play out in 2019. First of all the appetite for high-value, cross-functional collaboration across business departments, and externally with more employees in touch with customers and partners, will grow. Frontline workers will be at the forefront of transformation initiatives. Voice user interfaces and intelligent assistants will become prevalent in the workplace, with a wider availability of speech-enabled devices influencing adoption as enabling components for the digital employee experience. AI and ML will permeate communications and collaboration workflows in team collaboration, meeting room scenarios and individual employees’ interactions with digital assistants and voice user interfaces. Finally, we expect to see programmability define the next generation of business communications and collaboration technologies as vendors shift their focus from one-size-fits-all to flexible solutions with programmable capabilities that enable organizations to customize customer and employee interactions.
A second accompanying Preview report looks specifically at the trends we anticipate unfolding in workforce transformation.
451 Research’s 2020 Trends in Communications, Connectivity and Collaboration Technologies
Source: 451 Research, 2019
Methodology
Reports such as this one represent a holistic perspective on key emerging markets in the enterprise IT space. These markets evolve quickly, though, so 451 Research offers additional services that provide critical marketplace updates. These updated reports and perspectives are presented on a daily basis via the company’s core intelligence service, 451 Research Market Insight. Forward-looking M&A analysis and perspectives on strategic acquisitions and the liquidity environment for technology companies are also updated regularly via Market Insight, which is backed by the industry-leading 451 Research M&A KnowledgeBase.
Emerging technologies and markets are covered in 451 Research channels including Applied Infrastructure & DevOps; Cloud Transformation; Customer Experience & Commerce; Data, AI Analytics; Datacenter Services & Infrastructure; Information Security; Internet of Things; Managed Services & Hosting; and Workforce Productivity & Collaboration.
Beyond that, 451 Research has a robust set of quantitative insights covered in products such as Voice of the Enterprise, Voice of the Connected User Landscape, Voice of the Service Provider, Cloud Price Index, Market Monitor, the M&A KnowledgeBase and the Datacenter KnowledgeBase.
All of these 451 Research services, which are accessible via the web, provide critical and timely analysis specifically focused on the business of enterprise IT innovation. For more information about 451 Research, please go to www.451research.com.
451 Research’s 4SIGHT: Empowering the Digital Revolution
Throughout this report, you will see the below graphic indicating which of our 451 4SIGHT themes each trend relates to. 4SIGHT is 451 Research’s look into the future of information technology, organized around four main themes that we expect to shape the digital transformation agenda over the next 10 years and beyond. The 4SIGHT report is available to all clients via our research dashboard. For more information, visit our website.

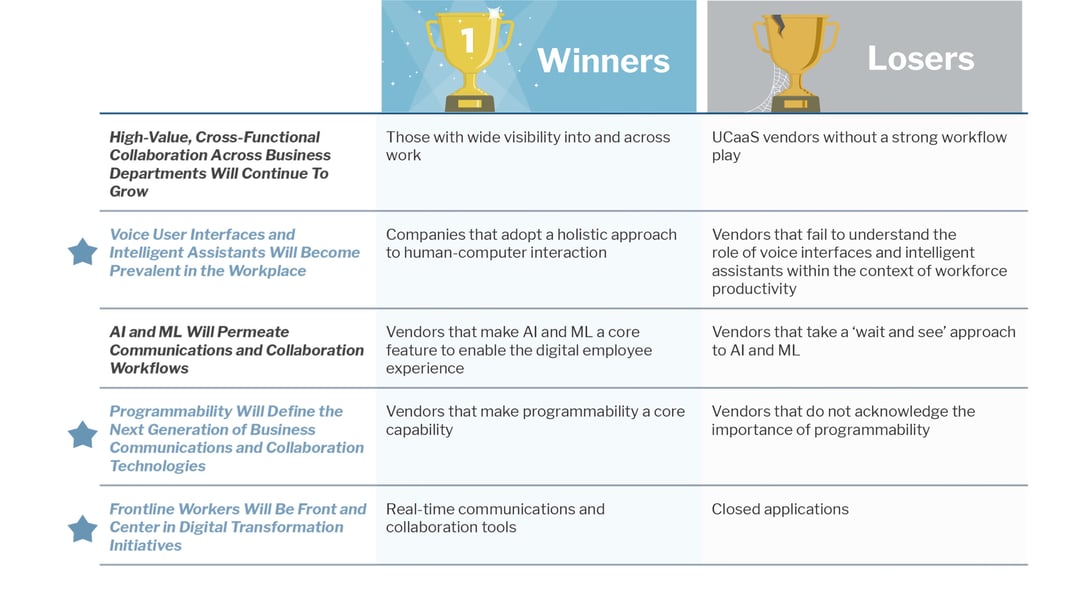
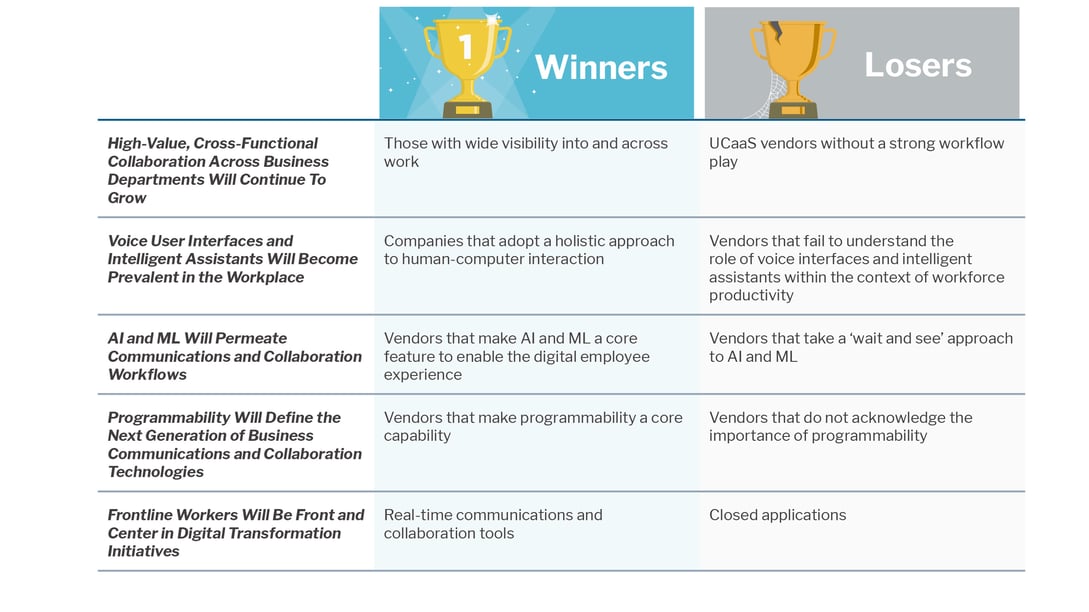
Trend 1: High-Value, Cross-Functional Collaboration Across Business Departments Will Continue To Grow
Implication: As business look for more operational agility and as autonomy and control around how work is designed decentralizes, there is a growing appetite for high-value, cross-functional collaboration across enterprises that will see more employees embrace new types of workflow, resource management practices and skills strategies across traditional reporting lines and hierarchies.

New cloud, social and mobile technologies are not just disrupting the way enterprise applications are designed, but also changing workplace behaviors and practices, echoing what has happened for consumers in their personal lives.
In businesses, this means outcomes are less specifically contingent on the discrete business divisions and the technologies serving them and more contingent on the degree to which enabling technologies can permit work to be imagined across those silos. It’s already a norm in many businesses for individual employees to belong to multiple different types of teams, some of which exist beyond their reporting line. The appetite for more of that kind of collaboration is growing, as is evident in our Voice of the Enterprise (VotE): Workforce Productivity & Collaboration, Work Execution Goals 2019 data, which shows 30% of C-level heads wanting their own team to collaborate more across departments.
Businesses will therefore have to organize to support individuals and teams operating within their own Venn diagrams of different work projects, work streams, initiatives and collaborations. As more of those circles form, involvement in each circle will likely introduce the end user to other adjacent circles, something that the system of delivery could play a role in intelligently orchestrating. This confirms our belief that the growth in appetite for more purposeful, high-value collaboration is one of the manifestations of the mainstreaming of agile principles across the workforce – that the best architectures, requirements and designs emerge from self-organizing teams, that businesspeople and technical people should be able to easily work together on projects, and that projects should be built around motivated, self-guided individuals.
One of the drivers of this is the emergence of new types of converged workspace providing wide horizontal visibility across the employee directory, and broader involvement in capabilities such as planning and resource management. The closer proximity of these capabilities to localized work initiatives will allow operational nodes – tight clusters of different skills, competencies and experience – to flexibly self-organize and have autonomy to execute more rapidly, responsively and in context. Self-organizing, multi-skilled teams – not individual lines of business (LOBs) – become the main organizational unit. LOBs could become the locales for the development of specialist skills that are infused into those teams as required. In this paradigm, teams organize around what they can accomplish on a project more than they organize daily in their LOB.
Recommendations
-
Be collaboration-first. With ownership over the design of work decentralizing while the need for more cross-organizational collaboration grows, how work happens is being re-written, and this dynamic needs to influence all vendors’ integration, workflow and usability strategies.
-
Consider partnering with a communications platform as a service (CPaaS) vendor. Collaboration is moving beyond point solutions and closer to the context of where work happens across more structured workflows. CPaaS vendors can provide the programmability in communications capabilities that will help make this happen.
Winners
-
Those with wide visibility into and across work. More people in their own work will be able to leverage and have input into capabilities such as planning and resource management that historically have been owned by fewer specialist users. Those vendors that own those democratizing levels of abstraction stand to benefit from more users and therefore wider possibilities for monetization as they offer higher and wider strategic value.
Losers
-
UCaaS vendors without a strong workflow play. While some UCaaS vendors do have this in their product roadmaps, some don’t show a strategy of prioritizing key integrations across other business-critical applications, nor the separate embeddable consumption of specific capabilities within other application experiences. That will lead to them being siloed and of diminishing value.
Trend 2: Voice User Interfaces and Intelligent Assistants Will Become Prevalent in the Workplace
Implication: Speech recognition has become mainstream in the eight years since Apple launched Siri with the iPhone 4S, influencing consumer familiarity with voice-enabled applications and digital assistants. This trend is now expanding into the enterprise, with a wider availability of speech-enabled devices influencing the adoption of voice user interfaces and intelligent assistants as enabling components for the digital employee experience.

We anticipate vendors and organizations will expand their use of voice interfaces and intelligent assistants for enterprise applications in 2020, with a focus on improving workplace productivity. We also expect organizations will explore their use for enhancing the digital employee experience, particularly for use cases that lead to efficiency and productivity improvements and where data input or real-time collaboration via a voice user interface is what works best.
When Siri first burst onto the scene with the iPhone 4S in October 2011, it led to expectations for the evolution of human-computer interaction, with keyboards and touch screens being displaced by voice commands on computers, smartphones and wearable devices. Voice has not displaced other user interfaces, but speech-enabled applications are increasingly available across a wide range of devices. Voice has also emerged as the main user interface for devices such as smart speakers, a category pioneered by Amazon with the launch of the Echo device in 2014.
When it comes to the enterprise segment, early deployments of voice user interfaces were initially driven by vertical-specific use cases. There are indications that enterprise adoption is becoming mainstream and expanding to include broad, horizontal use cases. According to 451 Research’s most recent VotE: Customer Experience & Commerce, Digital Transformation survey, voice user interfaces and digital assistants are among the top disruptive technologies that organizations plan to adopt within the next 24 months (see Figure 1).
Figure 1: Voice-Activated Interfaces and Digital Assistants Are Among the Top Disruptive Technologies for Tech Leaders
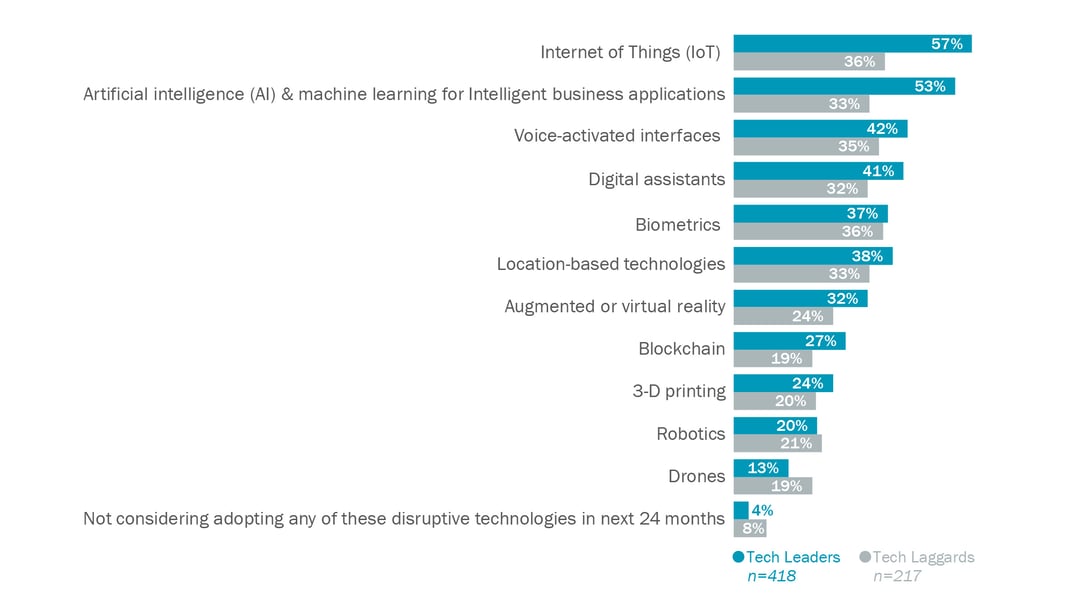
Source: 451 Research’s Voice of the Enterprise: Customer Experience & Commerce: Digital Transformation 2019
Q: Which of the following disruptive technologies does your organization plan to adopt over the next 24 months?
Several factors are coming together to influence enterprise adoption of voice interfaces and intelligent assistants, including the growing availability of speech-enabled devices and applications. Intelligent assistants like Alexa for Business (A4B), Google Assistant and Microsoft Cortana are increasingly available on many crossover devices including laptops, tablets and smartphones, as well as workplace-specific devices such as desk phones, meeting room equipment and hearable devices such as unified communications headsets from Poly and the recently announced Microsoft earbuds.
We are also seeing vendors expand their use of speech-enabled capabilities and intelligent assistants in horizontal applications. These include Microsoft, which recently unveiled new Cortana features for Outlook mobile that include Play My Emails (which reads aloud new emails) and a daily briefing email that provides a summary of upcoming meetings, relevant documents and reminders. Google Cloud also recently announced Google Assistant capabilities in G Suite that enable users to dial into a meeting and manage events in Calendar using voice commands.
Recommendations
-
Don’t overlook the growing relevance of voice interfaces and intelligent assistants for the digital employee experience. Voice user interfaces and intelligent assistants can have a significant impact for the digital employee experience, reducing friction by enabling workflow automation and simplifying access to business applications.
-
Ramp up market education efforts. Vendors face the challenge of educating the market on how to identify potential use cases for voice user interfaces and intelligent assistants and understanding the implications these can have for the digital employee experience.
Winners
-
Companies that adopt a holistic approach to human-computer interaction. Human-computer interaction is expanding to encompass new modalities such as gesture-based computing and voice commands. Together with intelligent assistants, these open opportunities to explore how employees can interact more effectively with technology.
Losers
-
Vendors that fail to understand the role of voice interfaces and intelligent assistants within the context of workforce productivity. Vendors should look beyond the consumerization market hype and embrace voice user interfaces and intelligent assistants as a long-term strategy that can help organizations redefine how employees interact with technology.
Trend 3: AI and ML Will Permeate Communications and Collaboration Workflows
Implication: AI and ML will permeate the roadmaps of business communications and collaboration providers, raising the profiles of traditional tools, such as unified communications, which will reposition as enabling components for the digital employee experience.
.jpg?width=1089&name=451_COVIDUpdate-2020-Workforce-Trends-14%20(1).jpg)
Figure 2: Digital Transformation Leaders Expect AI and Machine Learning Will Significantly Impact Their Organization’s Operations
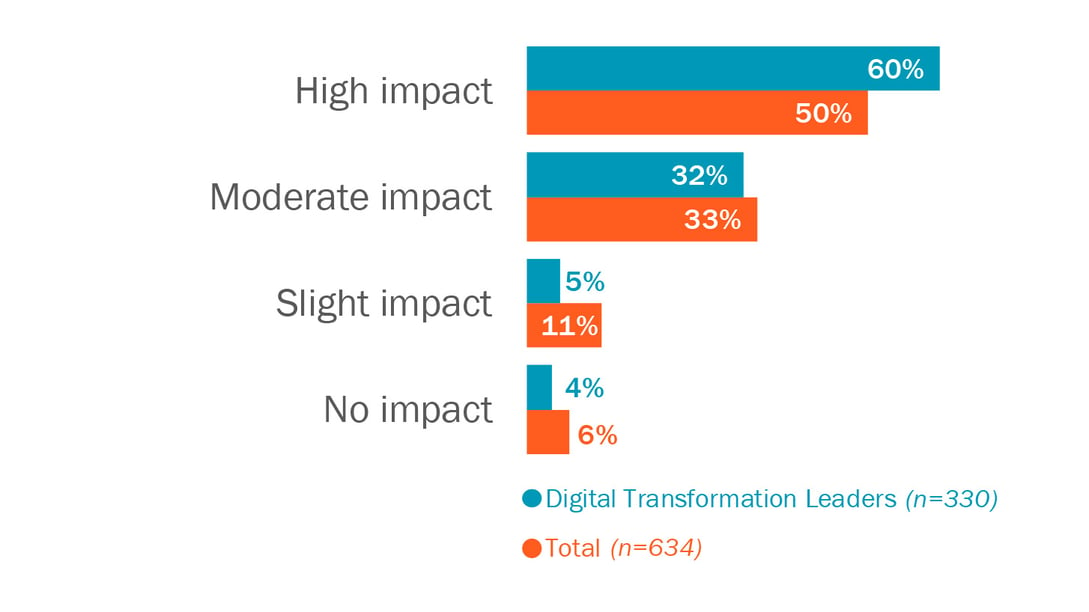
Source: 451 Research’s Voice of the Enterprise: Customer Experience & Commerce: Digital Transformation 2019
Q: Over the next 2 years, how much of an impact - if any - do you think each of the following will have on your organization’s operations? AI and machine learning capabilities
Providers of business communications and collaboration are not the exception. In the past two years, vendors such as Cisco, Google Cloud and Microsoft have included references to ‘intelligent communications’ and ‘contextual intelligence’ in their product updates. In addition to intelligent assistants and voice user interfaces, other areas where the use of AI and ML in communications and collaboration workflows is already evident include contextual intelligence to enhance the digital employee experience. Examples include Cisco Cognitive Collaboration, a set of AI-enabled capabilities in Cisco’s collaboration portfolio that include People Insights, which provides relationship intelligence about people and companies within Webex Meetings and Teams. And Microsoft recently announced Project Cortex, a new service that enables employees to easily access information within Office, Teams and Outlook without having to switch applications.
The former are technology leaders that are using AI and ML for competitive differentiation, but some of these capabilities are becoming commodified and increasingly available to other vendors. For example, Google Cloud’s Contact Center AI Solution is used by contact center vendors like 8x8, Avaya, Cisco, Five9, Genesys, Mitel and RingCentral to enable multichannel conversational user interfaces for live agents, chatbots and intelligent assistants. AWS provides an A4B integration for third-party device makers, allowing its intelligent assistant to be embedded on devices such as audio calling headsets and video conferencing systems. CPaaS providers such as Twilio and Vonage also play a role, making AI- and ML-enabled capabilities available via APIs.
These include capabilities to enhance team collaboration and the meeting room experience, such as automating dial-in to conference calls, setting up reminders, managing agendas and assigning action items and creating meeting summaries. As these capabilities become more commodified, providers of business communications and collaboration will incorporate them into their product roadmaps, raising the profile of tools like unified communications as an enabling component for the digital employee experience.
Recommendations
-
Vendors should reposition business communications within the context of the digital employee experience. Tools such as unified communications have been around for a long time, but are rapidly evolving with AI- and ML-enabled enhancements and emerging as a critical system of record for conversation that can support the digital employee experience.
-
Organizations should evaluate the use of cloud-based AI and ML for communications and collaboration. Vendors are making these capabilities available even for organizations that have not yet started or are still in the process of transitioning to cloud-based business communications.
Winners
-
Vendors that make AI and ML a core feature to enable the digital employee experience. Though still in its early days, AI and ML will change how employees communicate and collaborate with each other; this will redefine the competitive landscape for business communications and collaboration in the coming year.
Losers
-
Vendors that take a ‘wait and see’ approach to AI and ML. Technology leaders are using AI- and ML-enabled capabilities to differentiate, but these capabilities are becoming more commodified and set to become standard features for business communications and collaboration.
Trend 4: Programmability Will Define the Next Generation of Business Communications and Collaboration Technologies
Implication: CPaaS will influence the roadmaps of business communications and collaboration providers, which will shift their focus from one-size-fits-all to flexible solutions with programmable capabilities that enable organizations to customize customer and employee interactions.

The business communications and collaboration landscape has been increasingly influenced in recent years by CPaaS, a disruptive model for delivering programmable communications that enables developers to integrate real-time voice, video, chat and messaging into web and mobile applications. 451 Research believes programmable communications will play a key role in enabling the ‘liquid enterprise,’ which we define as a new breed of highly responsive, digital-native businesses. A distinctive element in these organizations will be ‘programmability,’ or the ability to manage workflows and applications in a highly customizable way. This represents a major shift in how organizations plan and execute work, as described in our August 2018 report, WorkOps: A primer on the new way of working.
IT decision-makers and LOB leaders are becoming increasingly aware of the relevance that programmability can have for business results. Our VotE: Workforce Productivity & Collaboration, Employee Lifecycle survey shows that agile architecture and codeless capabilities are emerging as key areas for future software investments by digital transformation leaders (see Figure 3).
Figure 3: Organizations Are Becoming Increasingly Aware of the Impact of Programmability for Business Results
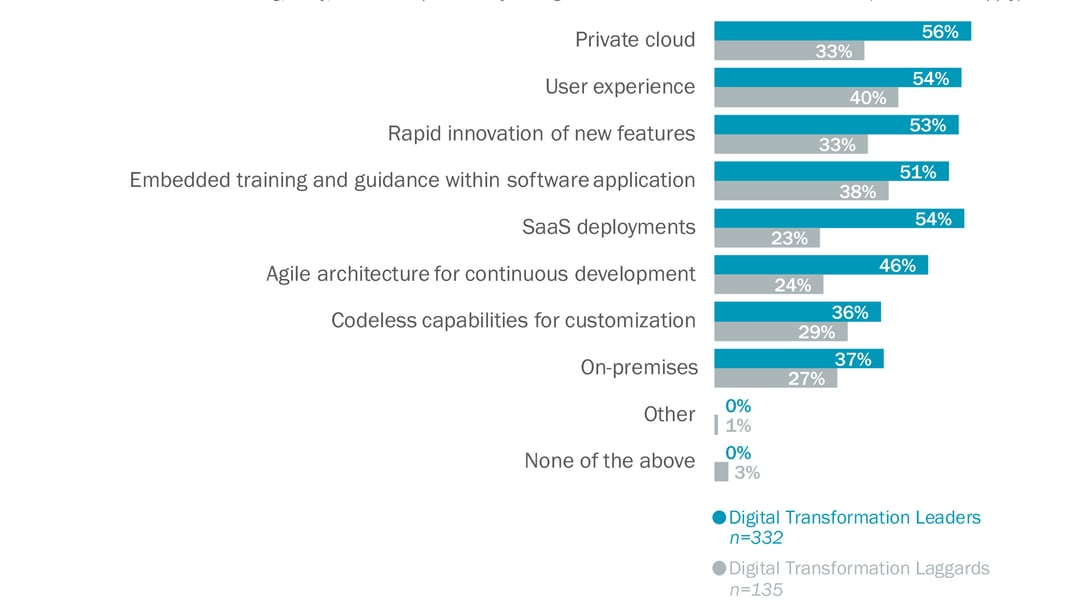
Source: 451 Research’s Voice of the Enterprise: Workforce Productivity & Collaboration, Employee Lifecycle 2019
Q: Which of the following, if any, are most important to your organization’s future software investments?
These trends increasingly encompass business communications and collaboration, resulting in a shift from siloed, ‘one-size-fits-all’ solutions – e.g., unified communications and contact center – to an ecosystem that enables intelligent, communications-enabled workflows for customer and employee interactions. The emerging software-defined business communications ecosystem will evolve based on a series of attributes we outline in the December 2018 report Communications PaaS: Turning Business Communications Inside Out.
This represents an important opportunity that will continue to grow as enterprise adoption of programmable communications takes off. Our CPaaS Market Monitor projects that the CPaaS segment will grow at a 33% CAGR, reaching $11.4bn by 2023. The mainstreaming of programmable communications has already sparked M&A activity, with seven CPaaS-related deals so far in 2019, according to 451 Research’s M&A KnowledgeBase. We anticipate further consolidation in the CPaaS space in 2020, driven by an ongoing interest in integrating real-time communications into business applications and workflows to streamline customer and employee interactions.
Recommendations
-
Organizations should consider programmability as a key feature for business communications. Rather than looking at these as a set of discrete applications, organizations should approach business communications as a set of tools that enable them to customize the ways in which they interact with customers and employees.
-
Vendors and service providers should look at programmability as the way forward. We don’t expect CPaaS will displace unified communications as a service (UCaaS) and contact center as a service (CCaaS), but these three categories are increasingly merging and overlapping with each other. This will lead vendors and service providers to incorporate programmability into their roadmaps and overall approach to business communications and collaboration.
Winners
-
Vendors that make programmability a core capability. Vendors that provide a hands-on approach and can make the technology easy to use for customers, rather than just jumping on the API bandwagon, should benefit from the growing market opportunity for programmable communications in the enterprise segment.
Losers
-
Vendors that do not acknowledge the importance of programmability. Programmability goes beyond merely providing API access; it entails developing and fostering an ecosystem that supports developers, startups and enterprise IT organizations.
Trend 5: Frontline Workers Will Be Front and Center in Digital Transformation Initiatives
Implication: Addressing the digital employee experience requirements for frontline workers will become increasingly relevant for organizations looking to deploy digital transformation initiatives. This will require organizations to redefine their approach for workplace communications to encompass their entire workforce.
.jpg?width=1089&name=451_COVIDUpdate-2020-Workforce-Trends-12%20(1).jpg)
Organizations are paying more attention to their frontline workforce – i.e., those workers who deal directly with customers or are closely involved in the production process. We anticipate that in 2020, organizations will expand their digital transformation initiatives to encompass the role frontline workers play in driving business outcomes.
The frontline workforce includes workers across many industries: In retail they include cashiers, sales representatives and customer service personnel; in manufacturing they are assemblers, fabricators and machine operators, along with their direct managers and supervisors; and in healthcare, anyone directly involved in the care and treatment of patients is considered a frontline worker, such as doctors, nurses, orderlies and aides working within medical facilities or externally providing at-home patient care. These workers have traditionally remained outside the scope of IT and business communications, largely due to the nature of their work.
However, there are indications that organizations are rethinking the role of the frontline workforce within the context of organizational culture and business agility. According to 451 Research’s 2H 2018 VoCUL: Corporate Mobility and Digital Transformation survey, a majority of early adopters of digital transformation initiatives consider it a top priority to make content across different repositories more easily searchable, shareable and usable by employees. This has led to the emergence of new approaches for workforce communications and collaboration that enable organizations to reach and engage 100% of their employee base, including frontline workers and remote employees.
We expect that in 2020, organizations will look to expand their digital transformation initiatives to provide contextually intelligent, personalized workplace communications encompassing their entire workforce. This will require a comprehensive approach to business communications and collaboration that includes real-time communications tools such as mobile messaging and push-to-talk applications, unified communications and the ‘next generation’ of the intranet.
Recommendations
-
Digital transformation initiatives should encompass frontline workers. Addressing the communications and collaboration requirements of frontline workers is not an easy task, given that it entails dealing with seasonal and temporary workers usually spread across different locations. However, in many cases they include customer-interfacing functions, and they are an integral part of the customer journey.
-
Vendors should adopt a solution-focused approach. Delivering a comprehensive solution encompassing the frontline workforce will require integrating different approaches to real-time communications.
Winners
-
Real-time communications and collaboration tools. Team collaboration and next-generation intranet have stolen the spotlight in recent years, but tools such as mobile messaging and push-to-talk provide distinct capabilities that are critical for use cases involving frontline workers.
Losers
-
Closed applications. Vendors that focus on the frontline workforce but fail to provide third-party integrations will be unable to provide the comprehensive solutions that customers increasingly require.
The Long View
New levels of abstraction in business apps are giving businesses ways to unlock the wellspring of their employees’ personal and collective creativity by decentralizing the autonomy over how consequential work is designed and executed. This is allowing them to imagine work beyond the confines of individual applications, which in turn is creating new business operational models. Communications and collaboration will be at the forefront of those new models.
However, this isn’t the current reality for most companies. Years of acceptance of dysfunctional technologies and implementation practices have left deeply embedded silos of people, information and process, and – perhaps most limiting – silos of mindset and imagination. The typical digital transformation narrative articulates the need for change, but it focuses too heavily on companies having formal digital strategies and centers of excellence, on IT’s role in technology adoption, and on the core IT infrastructure from which transformation benefits are often deemed to trickle down. It hasn’t spoken well to the hugely dynamic trend of businesses wanting to remove the daily friction in work to level up employees to do higher-value, more purposeful types of business-outcome-focused collaboration.
That needs a reverse perspective: one that’s bottom-up, more matrixed and people-centric, that leverages flexible and highly extensive communications capabilities to provide context into more structured workflows and processes. This shift has significant implications for how businesses conceive of, generate and execute against their goals; for the constitution of, definition of and interactions between their different lines of business and their respective technology stacks; and for how they steward the skills of their workforce.
We refer to the outcome of enterprise-wide agile at the corporate level as the ‘liquid enterprise.’ Within this model, technologies, practices and organizational designs enable businesses to react very fluidly to existing expectations and latent demand in their businesses’ target markets and the different competitive disruptions and innovations attempting to satisfy them. That’s the operational model fit for purpose in the digital age.
We believe this represents a shift in the center of gravity in enterprise software from systems of record and engagement to those platforms infusing comprehensive and intelligent communications capability into the work in the seams between and across those systems.
Further Reading
- 2020 Trends in Workforce Productivity & Collaboration: Workforce Transformation, December 2019
- Communications PaaS M&A expected to continue through 2020, November 2019
- Innovations in the user experience could trigger the next round of speech technology M&A, September 2019
- Workforce Productivity & Collaboration Market Monitor: CPaaS, August 2019
- WorkOps: A primer on the new way of working, August 2018
- Supporting the digital employee experience for frontline workers in healthcare, November 2019
- Supporting the digital employee experience for frontline workers in manufacturing, October 2019
- Cisco updates collaboration portfolio, positions Webex as digital transformation platform, August 2019
- Next ‘19: Google Cloud is redefining human computer interaction with voice user interfaces, April 2019
- VoCUL: Corporate Mobility and Digital Transformation (Representative), April 2019 AI and voice-enabled applications will change how we work in 2019, January 2019
- Voice of the Enterprise: Customer Experience & Commerce, Digital Transformation 2019, December 2019
- Voice of the Enterprise: Workforce Productivity & Collaboration, Employee Lifecycle 2019, December 2019
- Voice of the Enterprise: Workforce Productivity & Collaboration, Work Execution Goals and Productivity Challenges, October 2019
- Communications PaaS: Turning Business Communicatons Inside Out, December 2018
Analysts
- Raúl Castañón-Martínez, Senior Analyst, Workforce Collaboration and Communications
- Chris Marsh, Research Director, Workforce Productivity & Collaboration
/Ripcord%20Logo%20-%20Color%2011.png?width=2000&height=620&name=Ripcord%20Logo%20-%20Color%2011.png)